Unravel the mystery of subdomains and learn how they can revolutionize your website’s organization and functionality. Dive in now!

Image courtesy of via DALL-E 3
Table of Contents
Welcome to the world of the internet, where websites are like digital homes on a vast virtual landscape. Today, we’ll be diving into a fascinating topic that plays a crucial role in how websites are organized and accessed – subdomains. Let’s explore what a subdomain is, why websites use them, and how they fit into the fabric of the internet.
What is a Subdomain?
Let’s start with the basics. A subdomain is like a smaller neighborhood within a larger city. In the world of websites, a subdomain is a part of a website address that comes before the main domain name. For example, in the URL ‘blog.example.com,’ the ‘blog’ part is the subdomain. It helps to organize different sections or functions of a website, making it easier for users to navigate.
Why Do Websites Use Subdomains?
Websites use subdomains for a variety of reasons. They can be used to create distinct sections within a website, such as a blog, a store, or a forum. By using subdomains, website owners can keep different types of content separate and make it easier for visitors to find what they’re looking for. Subdomains also help with organization and can have benefits for search engine optimization (SEO), which we’ll explore later in this article.
Basic Structure of a URL
Understanding the Parts of a URL
A URL, which stands for Uniform Resource Locator, is the address of a specific resource on the internet. It is like a street address that helps you find a particular website. A URL has different parts that work together to bring you to the right place on the web.
The main parts of a URL include:
1. Protocol: This tells your web browser how to access the resource. The most common protocol is “http://” or “https://” which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
2. Domain: This is the main address of a website, like www.example.com. It’s like the main street where the website is located.
3. Subdomain: This is an optional part that comes before the main domain. It helps to organize different sections of a website. An example of a subdomain is blog.example.com, where “blog” is the subdomain.
4. Path: This part of the URL specifies the location of a specific page or file on the website. For example, www.example.com/blog is the path to the blog section of the website.
Where Does the Subdomain Appear?
The subdomain appears before the main domain in a URL. For instance, in the URL blog.example.com, “blog” is the subdomain that comes before the main domain “example.com.” This setup helps users and search engines understand the purpose of different sections of a website.
Examples of Subdomains
Subdomains are commonly used in website URLs to create distinct sections or services within a larger domain. For instance, a blog can have the subdomain ‘blog.example.com’ to host all its articles, while an online store can utilize ‘shop.example.com’ to showcase and sell products.
Why These Subdomains Are Used
The reason behind utilizing distinct subdomains like ‘blog.example.com’ is to enhance user experience by organizing content efficiently. This segregation allows visitors to navigate directly to the desired section. Similarly, ‘shop.example.com’ helps in creating a dedicated platform for e-commerce activities, streamlining the shopping process for customers.
How to Create a Subdomain
Before creating a subdomain, you first need to select the main domain under which the subdomain will be created. The main domain is like the parent folder where the subdomain will reside.
Image courtesy of via Google Images
Step 2: Access Domain Settings
Once you have chosen the main domain, you will need to access the domain settings of your website. This can usually be done through your web hosting provider’s control panel or domain registrar.
Step 3: Add Your Subdomain
Within the domain settings, you will find an option to add a subdomain. Here, you can input the desired name for your subdomain, such as “blog” or “shop”. Once you save the changes, your subdomain will be created and can be accessed using the URL format: subdomain.maindomain.com.
Benefits of Using Subdomains
When it comes to managing a website, utilizing subdomains can offer several advantages that contribute to a more organized and optimized online presence. Let’s explore some of the benefits of using subdomains:
Better Organization
Subdomains can help keep websites structured and easy to navigate. By creating separate subdomains for different sections or functions of a website, it becomes simpler for visitors to find the specific content they are looking for. For example, a website might have a subdomain for its blog, another for its e-commerce store, and yet another for its support resources. This segmentation makes it easier to manage and update each section independently, leading to a more coherent user experience.
Improved SEO
Search engines appreciate the clear organization that subdomains provide. When search engines crawl a website, they can better understand and index the content when it is neatly categorized into subdomains. This can result in better visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) for each section of the website. Additionally, using subdomains allows website owners to target specific keywords or topics more effectively, which can lead to higher rankings for relevant search queries.
Subdomains vs. Subdirectories
A subdirectory is a way to organize and structure content within a website. It is like a folder that holds specific files or information related to a particular topic or section of the website. Subdirectories are part of the main domain and appear as an extension of the main URL.
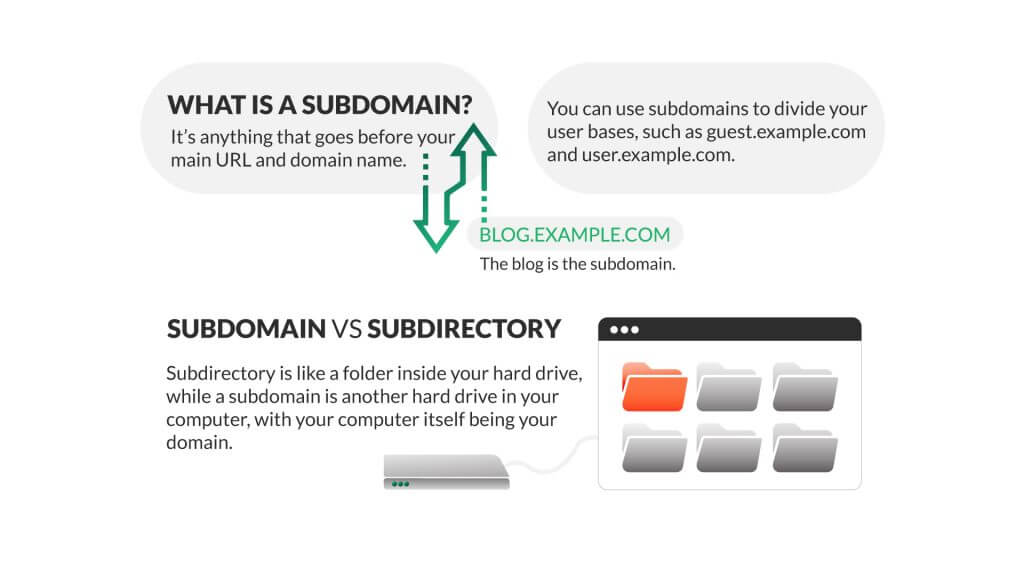
Image courtesy of via Google Images
Key Differences
One of the main differences between subdomains and subdirectories lies in their structure within a website. Subdomains create separate sections that are more distinct and independent, almost like having multiple websites under one domain. On the other hand, subdirectories are more integrated within the main website and share the same domain authority.
Additionally, subdomains can be beneficial for large companies or organizations that have distinct departments or branches that may function as separate entities. This separation allows for different branding, design, and content strategies tailored to each specific subdomain. Subdirectories, on the other hand, are often used for categorizing content or organizing information hierarchically within the main website.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to using subdomains for your website, there are a few common mistakes that can hinder your online presence. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can ensure that your subdomains work effectively to enhance your website’s organization and SEO. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
Using Too Many Subdomains
One common mistake many website owners make is creating an excessive number of subdomains. While subdomains can be useful for organizing different sections of your site, having too many can confuse visitors and dilute your website’s overall message. It’s important to strike a balance and only create subdomains when necessary for clear categorization and navigation.
Not Setting Up Properly
Another critical mistake to avoid is not setting up your subdomains properly. This includes ensuring that your DNS settings are correctly configured to point to the right servers. Failure to set up your subdomains correctly can lead to accessibility issues and impact your website’s performance. Make sure to double-check your settings and seek help from your hosting provider if needed to avoid this common error.
Advanced Tips for Subdomains
One advanced tip for optimizing your subdomains is to customize the content on each one. By tailoring the information and design of each subdomain to cater to specific audiences or purposes, you can enhance the user experience and improve engagement. For example, if you have a blog subdomain and a shop subdomain, you can ensure that the content on each is relevant and appealing to its target audience.
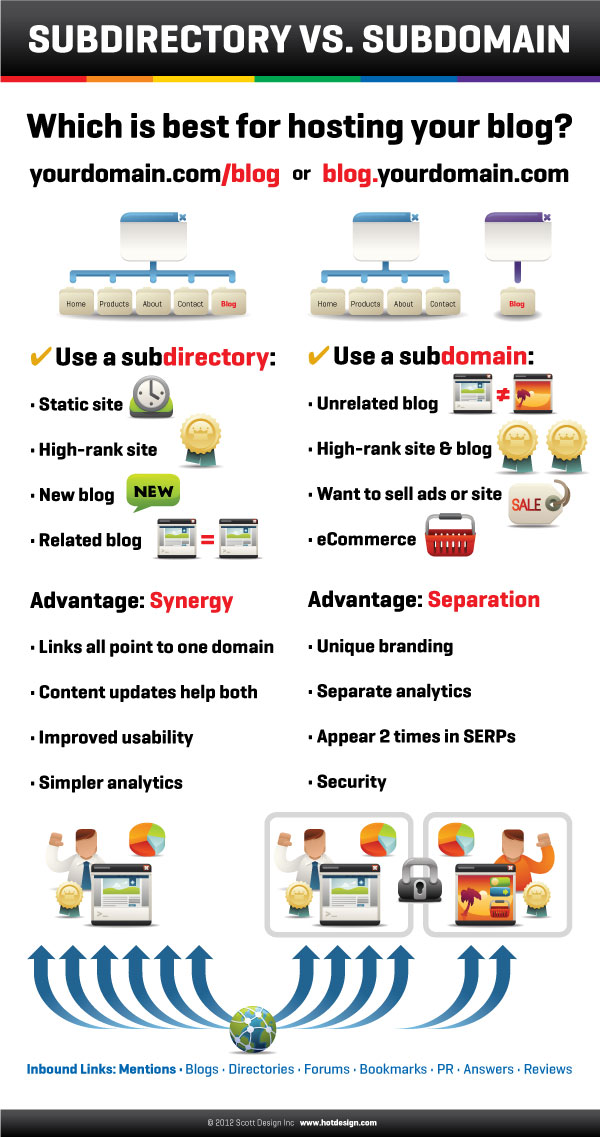
Image courtesy of via Google Images
Monitoring Performance
Another important aspect of managing subdomains is monitoring their performance. By keeping an eye on metrics such as traffic, conversion rates, and bounce rates for each subdomain, you can gain valuable insights into what is working well and what areas need improvement. This data can help you make informed decisions about how to optimize your subdomains for better results.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we delved into the world of subdomains and explored their significance in the online realm. A subdomain is like a small branch extending from the main tree of a website, giving each section its own unique address on the internet. By using subdomains, websites can better organize their content and potentially improve their search engine ranking.
Encouragement to Try
Now that you have a better understanding of what subdomains are and how they can benefit your website, why not give them a try? Experiment with creating subdomains for different sections of your website to see how it can help improve organization and user experience. Don’t be afraid to explore this aspect of website management and leverage subdomains to enhance your online presence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What if I Don’t Use a Subdomain?
If you choose not to use a subdomain, your website will default to the main domain. This means that all of your website content will be displayed under the primary domain name without any subdomain extension. While this may work for some websites, using a subdomain can offer more organization and flexibility in managing different sections of your site.
Can I have multiple subdomains?
Yes, you can have multiple subdomains for different sections or purposes on your website. Having multiple subdomains allows you to better organize your content and tailor each subdomain to its specific audience or function. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that having too many subdomains can lead to confusion and make it harder for users to navigate your site effectively.







